Types of Network Cables are essential components of modern connectivity in Dubai, UAE, and beyond. They facilitate data transfer between devices and networks, ensuring seamless communication. Ethernet cables (such as Cat 5e, Cat 6, and Cat 7) for wired connections and fiber optic cables for high-speed data transfer are examples of common varieties. These cables are the lifelines of the digital age, enabling businesses and individuals in Dubai and the UAE to stay connected and access the global network.
I. Types of Network Cables in Networking

- Ethernet Cable (Cat5e/Cat6): Common for wired LAN connections.
- Fiber Optic Cable: long-distance high-speed data transmission.
- Coaxial Cable: Used in cable TV and some broadband connections.
- HDMI Cable: Transmits audio and video for multimedia devices.
- USB Cable: Connects various devices, including routers and printers.
- Powerline Adapter: Uses electrical wiring for network connectivity.
- Patch Cable: Short Ethernet cables for interconnecting devices.
- Crossover Cable: Directly connects two devices without a switch.
- Optical Audio Cable (Toslink): digital audio signals are transmitted.
- VGA Cable: Analog video connection for older displays.
II. 4 Types of Networking Cables
- Unshielded twisted pair (UTP): The most typical networking cable is UTP, which is used in most residences and companies. To lessen interference, they are constructed from four pairs of copper wires that have been twisted together. UTP cables are reasonably priced and simple to install.
- Shielded twisted pair (STP): STP cables resemble UTP cables, except each pair of wires is protected by an extra metal shield. The disturbance from other electronic equipment is lessened thanks to this shield. Although STP cables cost more than UTP cables, they are also more resilient and less prone to interference.
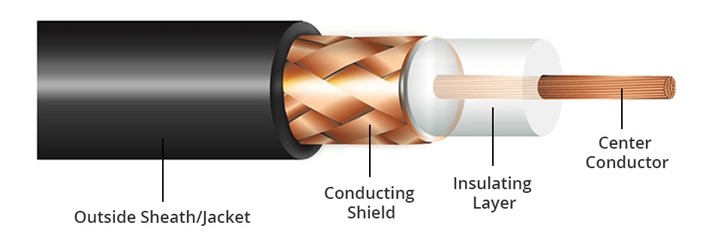
- Coaxial cable: A center copper conductor surrounded by an insulating layer and a braided metal shield make up coaxial cables. Coaxial cables were once the most common type of networking cable, but they have been largely replaced by UTP and STP cables. Some applications, including cable TV and satellite TV, nevertheless make use of coaxial lines.
- Fiber optic cable: Instead of using electrical impulses to convey data, fiber optic connections use light signals. The Internet backbone and other high-speed networks frequently use fiber optic cables since they are the fastest type of networking wire. Although fiber optic cables are more expensive than other networking cables, they are also more resilient to interference and longer-lasting.
III. Types of Network Cables with Examples

1. Network cables:
- Coaxial: RG-58, RG-6, RG-11
- Twisted pair: UTP, STP, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a
- Fiber optic: Single-mode, multi-mode
2. Examples:
- Coaxial: Used in older cable TV and Ethernet networks
- Twisted pair: The most typical network cable used in residences and workplaces
- Fiber optic: Fastest network cable for data transmission and high-speed internet use
Depending on your unique needs and requirements, you may require a certain kind of network cable. For instance, if a cable is required for a home network, UTP Cat5e or Cat6 cable is a good option. If you need a cable for a high-speed internet connection, fiber optic cable is the best choice.
A. How Network Cables?

A network cable is a physical cable that connects devices to a computer network. It has a standard length of 100 meters (328 feet) and is constructed of copper wires. Electrical signals are used to convey data through network links. After that, the data is packetized and transmitted over the network. The original data is put back together once the packets have arrived at their destination.
B. What Are The 3 Main Cables in Networking?
The three main networking cables are Ethernet (Cat5e/Cat6), Fiber optic, and Coaxial cables. They transmit data through wired connections in various networking applications.